Atherosclerosis is a process in which fats and cholesterol accumulate on the arteries’ walls alongside inflammatory cells, smooth muscle cells, and connective tissue creating plaques, limiting blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart, brain, or other organs. These plaques may suddenly rupture and block flow resulting in heart disease, chest pain, heart attack, or stroke.
Atorvastatin is a medication that slows down the production of cholesterol and helps stabilize plaques, preventing rupture and preventing these life-threatening conditions. Still, atorvastatin interacts with many medications, requiring monitoring or dose adjustment. (1-2)
This article covers atorvastatin interactions with drugs and food. Keep reading to learn about the interactions of the medication you should use for a long time and what combination to avoid.
1. Cyclosporine or Gemfibrozil
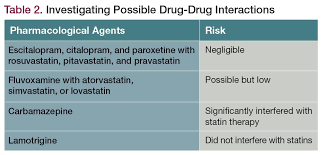
Cyclosporine and gemfibrozil significantly increase atorvastatin plasma levels and the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis; therefore, the concomitant use of these medications is not recommended. (1)
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) plays a vital role in atorvastatin breakdown. It is present in the liver and intestine and, aside from atorvastatin, is crucial for the metabolism of about half of the marketed drugs. (2-3)
Gemfibrozil is another medication used to lower triglycerides and cholesterol. By this mechanism, gemfibrozil prevents heart attacks and reduces the risk of pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia. When used alone, gemfibrozil may cause myopathy; however, the risk is much higher if coadministered with a statin. (4)
Patients who have undergone organ transplantation may need to take cyclosporine, a medication that helps the body not to reject the transplanted organ. While suppressing the immune system, cyclosporine, at the same time, inhibits CYP3A4. (1, 5)
Atorvastatin, when used as a monotherapy, may cause the following side effects:
Myopathy – a condition where the skeletal muscles are affected. The enzyme creatine kinase levels increase due to muscle damage, alongside muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness; (6)
Rhabdomyolysis – extreme amounts of proteins (especially myoglobin) and electrolytes are released in the blood from the damaged muscle tissue. This can lead to kidney damage. (7)
2. Other Fibrates
Gemfibrozil belongs to fibrates, a class of lipid-regulating medications. Similar to gemfibrozil, other fibrates may cause myopathy when given alone. When atorvastatin is used with other fibrates, the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis increases. (1, 4)
If your doctor considers that the combination treatment of atorvastatin and other fibrates is more beneficial than the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, concomitant use is acceptable. If so, your doctor will monitor your condition for signs and symptoms of myopathy, especially when initiating therapy and titrating the dose of both drugs. (1)
Statin-induced muscle pain and myopathy are typically symmetric and proximal (closer to the torso). As such, shoulders, upper arms, hips, and thighs are commonly affected, and there may be functional impairments such as difficulty raising arms above the head, standing from a seated position, or climbing stairs. (8)
3. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications treat viral infections like AIDS (HIV), Cold Sores (Herpes), Ebola, or COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Some antiviral drugs can inhibit CYP3A4 and/or drug transporters (e.g., BCRP, OATP1B1/1B3, P-gp, MRP2, and/or OAT2). This effect can significantly increase atorvastatin plasma levels, leading to myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. (1, 9)
4. Several Azole Antifungals or Macrolide Antibiotics
Some azole antifungals or macrolide antibiotics are other CYP3A4 inhibitors that increase atorvastatin plasma levels.
Azole antifungal drugs that eliminate fungal pathogens and inhibit cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes are:
Fluconazole;
Itraconazole;
Clotrimazole;
Miconazole; and
Ketoconazole. (10)
Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that treat specific bacterial infections which can cause pneumonia, sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, uncomplicated skin infections, and otitis media (ear infection). Macrolide antibiotics also inhibit CYP3A4. Inhibitory effects of macrolides or select azole antifungals significantly increase atorvastatin plasma levels, which may cause myopathy. (11-121)
5. Food: Niacin and Grapefruit Juice
Niacin, aka vitamin B3, helps convert nutrients into energy and supports making “good” cholesterol. It is available in food sources such as:
Milk;
Meat;
Yeast;
Cereals.
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin, so if you consume more than the body needs, it will be excreted in the urine. Niacin can also be prescribed in high doses to help lower cholesterol. High doses of prescribed niacin can cause side effects and interact with medications, including atorvastatin. (13)
There are reports of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis cases when ≥1 gram/day of niacin was taken with atorvastatin. (14)
ADVERTISEMENT
Your doctor may consider that the benefit of the concomitant use of atorvastatin outweighs the increased risk of side effects. If you take niacin and atorvastatin, be aware of myopathy’s signs and symptoms explained earlier. (1)
While niacin co-administration can be acceptable, high quantities of grapefruit juice are not recommended. (1)
Grapefruit juice is generally healthy and safe in your diet. It is also rich in vitamin C and potassium. However, it interacts with many medications, including atorvastatin, because it blocks the CYP3A4 enzyme activity. The result is an increased level of atorvastatin in the body and a higher risk of side effects. (15)
Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration recommends avoiding Seville oranges, pomelos, and tangelos because of the same effect they have as grapefruit juice. (15)
6. Rifampin
The interactions explained above are due to the inhibition of the CYP3A4 enzyme. Unlike the above medications, rifampin induces cytochrome P450 3A4 but inhibits OATP1B1. This effect can lead to the opposite, a reduction of atorvastatin plasma concentrations or an increase in atorvastatin concentrations. (16, 17)